1. Introduction
Networking is a fundamental aspect of modern computing that enables communication and data exchange between devices. Networks are categorized based on their size, geographical coverage, and the technologies used. Three primary types of networks are Local Area Network (LAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), and Wide Area Network (WAN). Understanding these network types is crucial for both IT professionals and students.
2. Definitions
a. Local Area Network (LAN):
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices within a limited geographic area, such as a home, office, or campus. LANs are characterized by high data transfer rates, low latency, and the ability to connect multiple devices like computers, printers, and servers within a close proximity. LANs typically use Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi for connectivity.
b. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) spans a larger geographical area than a LAN, typically covering a city or a large campus. MANs are designed to interconnect multiple LANs within a specific region, providing efficient communication and data transfer over longer distances. MANs are often used by organizations with multiple locations within a city to ensure seamless data exchange.
c. Wide Area Network (WAN):
A Wide Area Network (WAN) covers an even larger geographical area, such as a country, continent, or even the entire globe. WANs are designed to connect multiple LANs and MANs, enabling communication between devices across vast distances. The Internet is the most well-known example of a WAN. WANs use various technologies, including leased lines, satellite links, and public networks, to facilitate long-distance communication.
3. Examples
a. Local Area Network (LAN):
– Example 1: A small business office where all computers, printers, and servers are connected via Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi, allowing employees to share resources and communicate internally.
– Example 2: A home network where multiple devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and smart TVs, are connected to a single router, enabling them to access the internet and communicate with each other.
b. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
– Example 1: A university campus network that connects various departments, libraries, and administrative buildings within the campus area, allowing seamless communication and resource sharing among students and faculty.
– Example 2: A city’s public Wi-Fi network that provides internet access to residents and tourists across multiple hotspots within the city.
c. Wide Area Network (WAN):
– Example 1: A multinational corporation with offices in different countries uses a WAN to connect its global network, allowing employees to collaborate and share data across continents.
– Example 2: The Internet, which connects millions of networks worldwide, enabling communication, data exchange, and online services across the globe.
4. Diagrams
a. Local Area Network (LAN) Diagram:
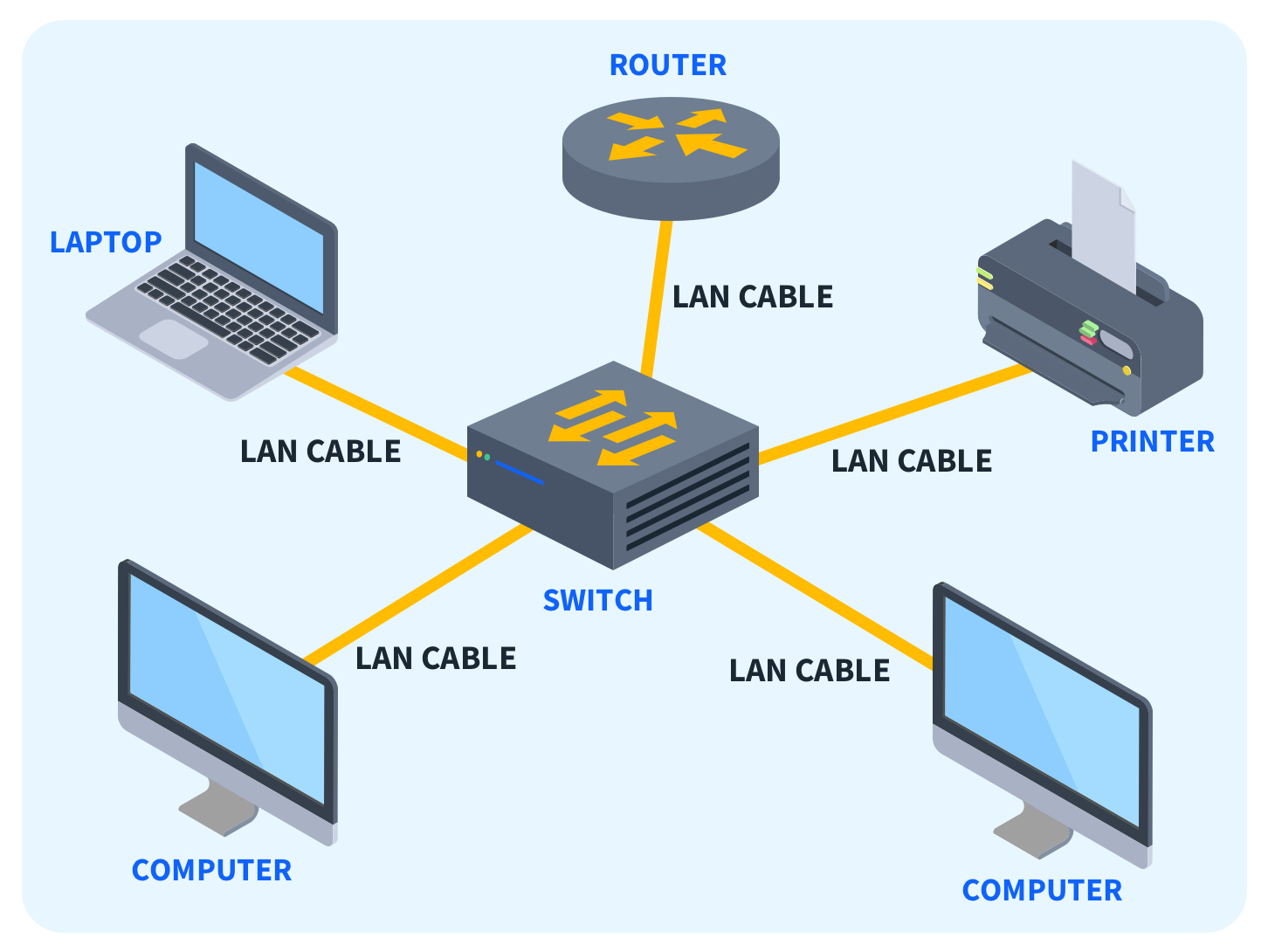
b. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Diagram:

c. Wide Area Network (WAN) Diagram:
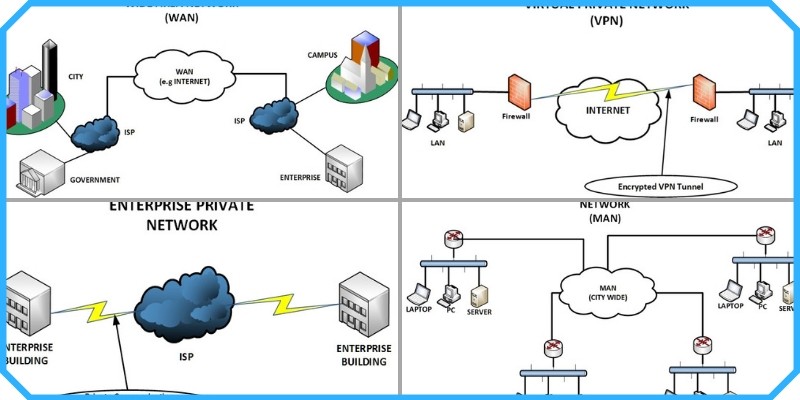
5. 15 Questions
1. What is a Local Area Network (LAN)?
2. How does a LAN differ from a WAN?
3. Describe the primary purpose of a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN).
4. Give an example of where a MAN might be used.
5. What is the most common technology used in LANs?
6. How do devices in a LAN communicate with each other?
7. Explain the role of a router in a LAN.
8. How does a MAN connect multiple LANs?
9. What are some advantages of using a WAN?
10. Describe a scenario where a WAN would be necessary.
11. What is the main difference between MAN and WAN in terms of coverage?
12. How does the Internet function as a WAN?
13. What are some challenges associated with managing a WAN?
14. Explain how a university campus network can be classified as a MAN.
15. What factors influence the choice between implementing a LAN, MAN, or WAN?
Q1. What is a Local Area Network (LAN)?
Answer: A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or a small group of buildings. The primary purpose of a LAN is to enable devices to communicate and share resources like files, printers, and internet connections efficiently.
Q2. How does a LAN differ from a WAN?
Answer: A LAN (Local Area Network) is typically confined to a small area, like a single building or campus, and allows high-speed communication between connected devices. In contrast, a WAN (Wide Area Network) spans a much larger geographical area, such as a city, country, or even globally, and connects multiple LANs. WANs usually have lower data transfer speeds and higher latency compared to LANs due to the greater distances involved.
Q3. Describe the primary purpose of a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN).
Answer: The primary purpose of a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is to connect multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) within a city or a large campus. MANs are designed to provide high-speed connectivity across a larger area than a LAN, making it ideal for organizations with several buildings spread across a city.
Q4. Give an example of where a MAN might be used.
Answer: A MAN might be used by a university with multiple campuses spread across a city. The MAN would connect the individual LANs of each campus, enabling seamless communication and resource sharing among all campuses.
Q5. What is the most common technology used in LANs?
Answer: The most common technology used in LANs is Ethernet. Ethernet cables and switches are widely used to establish wired connections between devices in a LAN. Additionally, Wi-Fi (Wireless LAN) is also commonly used to provide wireless connectivity within a LAN.
Q6. How do devices in a LAN communicate with each other?
Answer: Devices in a LAN communicate with each other using network protocols, primarily the Ethernet protocol for wired connections or Wi-Fi for wireless connections. Data is transmitted in packets over the network, and devices use MAC addresses to identify each other. A switch or hub typically manages the data flow within the LAN.
Q7. Explain the role of a router in a LAN.
Answer: A router in a LAN serves as a gateway between the local network and external networks, such as the internet. It routes data between the LAN and other networks, ensuring that data sent from a device in the LAN reaches the correct destination outside the LAN. The router also assigns IP addresses to devices in the LAN and manages traffic to optimize network performance.
Q8. How does a MAN connect multiple LANs?
Answer: A MAN connects multiple LANs using high-speed fiber optic cables, microwave links, or wireless technologies. The MAN infrastructure is typically owned and managed by a service provider or a large organization. It enables communication between LANs by providing a high-capacity backbone network that interconnects the individual LANs across the city or region.
Q9. What are some advantages of using a WAN?
Answer: Some advantages of using a WAN include:
- Broad Geographical Coverage: WANs enable communication and resource sharing across vast distances, connecting multiple LANs globally.
- Centralized Data: Organizations can centralize their data and applications in one location and provide access to remote offices or users worldwide.
- Scalability: WANs can easily scale to connect new locations, making it suitable for growing businesses.
Q10. Describe a scenario where a WAN would be necessary.
Answer: A WAN would be necessary for a multinational corporation with offices in different countries. The WAN would connect all the offices, enabling employees in various locations to access the company’s central servers, share files, and communicate effectively, regardless of their geographical locations.
Q11. What is the main difference between MAN and WAN in terms of coverage?
Answer: The main difference between MAN and WAN in terms of coverage is the geographical area they span. A MAN typically covers a city or a large campus, connecting multiple LANs within that area. In contrast, a WAN covers a much larger area, such as multiple cities, countries, or even continents, connecting multiple MANs and LANs.
Q12. How does the Internet function as a WAN?
Answer: The Internet functions as a WAN by connecting millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks worldwide. It allows computers and devices across the globe to communicate with each other, access resources, and share information. The Internet uses various networking technologies, including fiber optics, satellite links, and undersea cables, to create a vast, interconnected network.
Q13. What are some challenges associated with managing a WAN?
Answer: Some challenges associated with managing a WAN include:
- High Costs: WANs require significant investment in infrastructure, such as leased lines, and ongoing maintenance.
- Complex Security: Due to the vast area covered and the multiple networks involved, securing a WAN is complex and requires robust encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Latency and Reliability: The greater distances and multiple network hops involved in WAN communication can lead to higher latency and potential reliability issues.
Q14. Explain how a university campus network can be classified as a MAN.
Answer: A university campus network can be classified as a MAN if it connects multiple LANs spread across different buildings or campuses within a city. The network typically uses high-speed connections, such as fiber optics, to link the LANs, allowing seamless communication and resource sharing between different parts of the university.
Q15. What factors influence the choice between implementing a LAN, MAN, or WAN?
Answer: Factors influencing the choice between implementing a LAN, MAN, or WAN include:
- Geographical Coverage: The area that needs to be covered will determine the type of network. LANs are for small areas, MANs for cities, and WANs for global connections.
- Data Transfer Needs: The required speed and latency will affect the choice. LANs offer the highest speeds with the lowest latency.
- Cost: Budget constraints will impact the decision. WANs are typically more expensive to implement and maintain than LANs or MANs.
- Security Requirements: The level of security needed may influence the choice, with WANs generally requiring more complex security measures.
- Management Complexity: The complexity of managing the network also plays a role, with WANs being the most complex to manage due to their size and the number of interconnected networks.
Comparison Table: LAN, MAN, WAN
| Feature | Local Area Network (LAN) | Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) | Wide Area Network (WAN) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geographical Coverage | Limited to a small area (e.g., home, office) | Covers a city or large campus | Covers a large area (e.g., country, globe) |
| Data Transfer Speed | High (up to 10 Gbps or more) | Moderate (up to 1 Gbps) | Varies (from 56 Kbps to 100 Gbps) |
| Latency | Low | Moderate | High |
| Connectivity | Ethernet, Wi-Fi | Fiber optics, wireless | Leased lines, satellite, public networks |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | High |
| Management Complexity | Low | Moderate | High |
| Example | Office network, home network | University campus network, city Wi-Fi | Internet, multinational corporate network |
| Ownership | Typically private | Can be private or public | Often managed by service providers |
| Security | Easier to secure | Requires robust security measures | Highly complex security requirements |
| Fault Tolerance | High (due to smaller scale) | Moderate (dependent on infrastructure) | Lower (due to vast coverage) |
7. Conclusion
Understanding the differences between LAN, MAN, and WAN is crucial for designing and implementing effective network solutions. LANs are ideal for small-scale, localized networking needs, while MANs serve medium-sized areas such as cities or campuses. WANs are essential for connecting networks across large distances, enabling global communication and data exchange. By knowing the strengths and limitations of each type, organizations can choose the most appropriate network to meet their specific requirements.
FAQ: LAN, MAN, WAN
Q1: What is a LAN?
A: A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices within a limited area such as a home, office, or small group of buildings. It allows for high-speed communication and resource sharing among connected devices.
Q2: How does a LAN differ from a MAN?
A: A LAN is limited to a small geographic area, while a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) covers a larger area, such as a city or a large campus, and connects multiple LANs within that area.
Q3: What are common uses of a MAN?
A: MANs are typically used to connect various LANs within a city or large campus, such as connecting different branches of a university or multiple government offices within a city.
Q4: What is the main difference between MAN and WAN in terms of speed?
A: MANs generally offer higher speeds than WANs, as they cover a smaller area with more focused infrastructure. WANs cover larger distances, which can result in slower speeds and higher latency.
Q5: Can Wi-Fi be used in a LAN?
A: Yes, Wi-Fi is commonly used in LANs to provide wireless connectivity to devices within the network, allowing them to communicate without the need for physical cables.
Q6: Why would an organization use a WAN?
A: An organization would use a WAN to connect offices or branches located in different cities, countries, or continents, enabling communication and resource sharing across large distances.
Q7: What role does a router play in a LAN?
A: A router in a LAN connects the local network to external networks, such as the internet. It manages traffic between the LAN and other networks, ensuring that data reaches the correct destination.
Q8: How is security managed in a WAN?
A: Security in a WAN is managed through various measures, such as encryption, firewalls, and virtual private networks (VPNs), to protect data as it travels over long distances and through multiple networks.
Q9: What are some examples of where a WAN might be necessary?
A: WANs are necessary for multinational corporations, internet service providers, and government agencies that need to connect offices, data centers, or users across different regions or countries.
Q10: How does the internet function as a WAN?
A: The internet functions as a WAN by interconnecting millions of networks globally, enabling devices to communicate and share resources regardless of their location.
Q11: What are the primary technologies used in MANs?
A: MANs often use high-speed fiber optic cables, microwave links, and wireless technologies to connect multiple LANs across a city or large campus.
Q12: What are the advantages of using a LAN?
A: Advantages of using a LAN include high data transfer speeds, low latency, ease of management, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to securely share resources like files, printers, and internet access within a small area.
Q13: What challenges are associated with managing a WAN?
A: Challenges of managing a WAN include high costs, complex security requirements, potential latency issues, and the difficulty of maintaining consistent performance across large distances.
Q14: How does a MAN connect different LANs?
A: A MAN connects different LANs by using a high-capacity backbone network, often composed of fiber optics or wireless connections, allowing for efficient data transmission across the connected LANs.
Q15: What factors determine whether a LAN, MAN, or WAN should be implemented?
A: Factors include the geographical area to be covered, data transfer speed requirements, cost, security needs, and the complexity of network management. The choice depends on the specific needs and scope of the network deployment.

Comments are closed.